Allevi Blog
Allevi Author: New Platelet-Rich Bioink Boosts Healing
- Updated on April 9, 2020
New #AlleviAuthor coming at you! Platelets are a component of blood that play a crucial role in wound healing: they induce clotting! Remember the last time you nicked yourself with a kitchen knife? The platelets in your blood rushed to the site of the wound and coagulated to staunch the bleeding and start the healing process. But platelets don’t stop there – they also release growth factors to help repair the tissue which is why it is increasingly common to mix them with plasma for use in the treatment of wound care and post-operative procedures.
Researchers at MIT, University of Nebraska-Lincoln, and Massachusetts General Hospital used the Allevi #BetaBot to develop a platelet-rich bioink to boost the healing properties of 3D printed tissues and skin grafts.
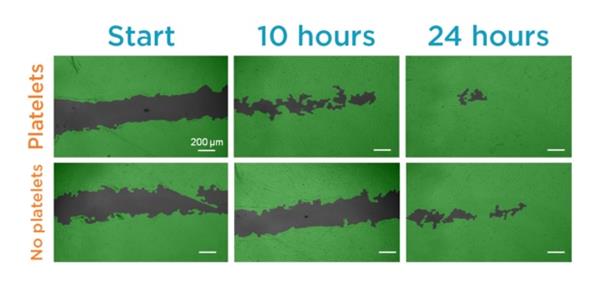
“In less than a day, the platelet-rich ink had prompted enough cell migration to heal about 50 percent of a scratch on some artificial skin, whereas the platelet-less version had covered just 5 percent of it. The ink also demonstrated the other unique property that platelets can offer, which is its ability to call for ‘reinforcement’ cells. It encouraged more than twice as many mesenchymal stem cells to migrate towards it than the platelet-less version, in a 24-hour period. These stem cells can then develop into muscle, cartilage or bone.” 🅰️🅱️🆎🅾️
As the field of 3d bioprinting matures, a platelet-rich bioink like this one will be crucial for organ replacement procedures to help with wound healing and tissue regeneration.
Their findings were published in Advanced Healthcare Materials.

