Overview
Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid), or PLGA, is a common thermoplastic used in bioprinting for its tunable degradability and mechanical properties. The degradation and mechanical properties of this material can be altered by adjusting the ratios of the copolymers polylactide and polyglycolide. Thermoplastics in bioprinting are often used as a support structure to provide extra mechanical strength for hard tissues and as reinforcement for matrix bioinks. Follow this step-by-step protocol for bioprinting hard tissues using PLGA.
Materials
- PLGA
- Metal tips
- Petri dish or well plate for printing
- Stainless Steel Allevi Syringe (5mL or 10mL)
- Suggested: painter’s tape for improved first layer adhesion
Methods
- Load PLGA into a metal syringe;
- Screw the metal tip on the syringe;
- Set your Allevi CORE™ extruder temperature to 100˚C;
- Load your syringe into the extruder;
- Wait for approximately 20 min until the PLGA melts before starting to print.
Print Settings: PLGA Protocol
| Speed (mm/s) | Layer height (mm) | Nozzle Diam (mm) | Gauge |
| 1.0 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 30 |
| Pressure (psi) | Crosslink (sec) | Print Temp (°C) |
| 100 | 0 | 100 |
Note: different gauges require different pressure and yield different resolutions.
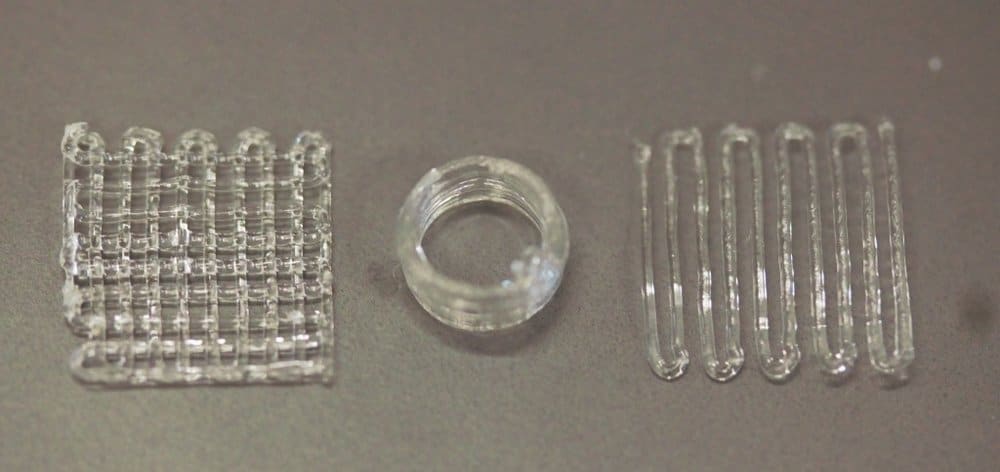

We hope you found this protocol helpful for bioprinting hard tissues using PLGA! Click here for more bioprinting protocols.

