Allevi Blog
A Novel Cartilage Implant Based on a Combination of 3D Printing and Biomaterial Design Strategies
- Updated on July 13, 2022
The field of regenerative medicine in joint disorders has progressed in the last month with help from researchers at Trinity College Dublin in Dublin, Ireland. Researchers from the Centre for Biomedical Engineering created a novel articular cartilage scaffold for potential off-the-shelf use in synovial joint regeneration implants.
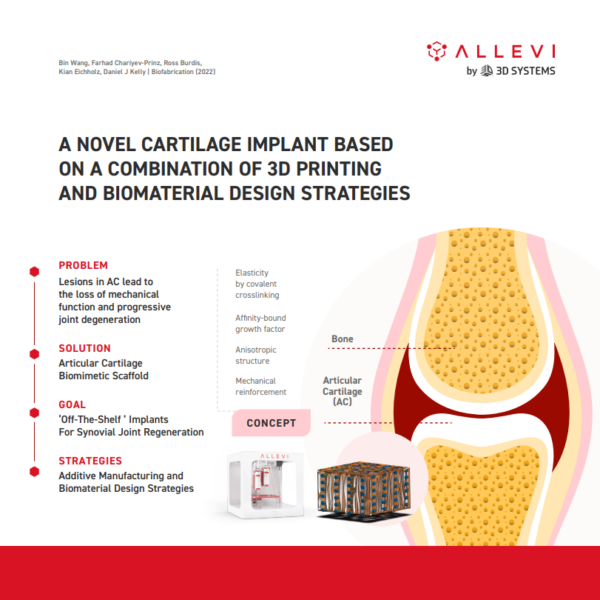
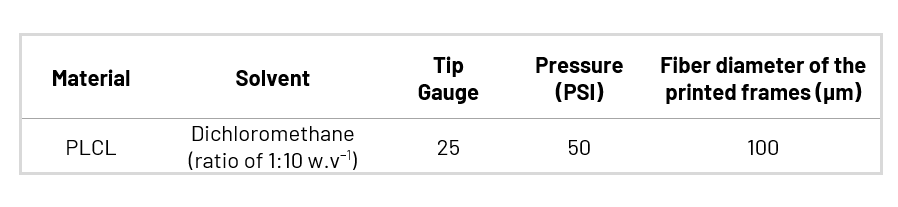
This articular cartilage was created through the integration of additive manufacturing techniques with biomaterial design strategies. To produce a scaffold with a biochemical composition and architecture similar to native cartilage tissue, researchers used a combination of alginate and alginate sulfate (covalently crosslinked hydrogels) with an anisotropic porous structure fabricated by a directional freezing technique. To achieve the mechanical properties compatible with the articular cartilage, the alginate/alginate sulfate hydrogel was reinforced with a 3D printed poly(lactide-co-ε-caprolactone) (PLCL) structure. Using our Allevi 2 bioprinter, researchers presented a solvent-based printing of PLCL that successfully allowed the printing of frameworks of this polymer without any need for high melting temperatures. The print parameters utilized on the Allevi 2 were the following:
These findings highlight the ability of this mechanically reinforced composite scaffold to stimulate cellular infiltration and chondrogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells, to guide the orientation of the newly deposited extracellular matrix (rich in sulfated glycosaminoglycan and type II collagen), and to support and control the release of growth factors (TGF-β3) (results obtained from in vitro tests in either static or dynamic conditions).
Although additional research and in vivo experimentation is required, this new technique of incorporating biofabrication strategies is undoubtedly a promising step towards the fabrication of biomimetic regenerative implants for articular cartilage repair.
You can read the complete publication, “Additive manufacturing of cartilage-mimetic scaffolds as off-the-shelf implants for joint regeneration” in the Biofabrication journal. To read more publications by Allevi Authors, check out the Allevi Blog!

