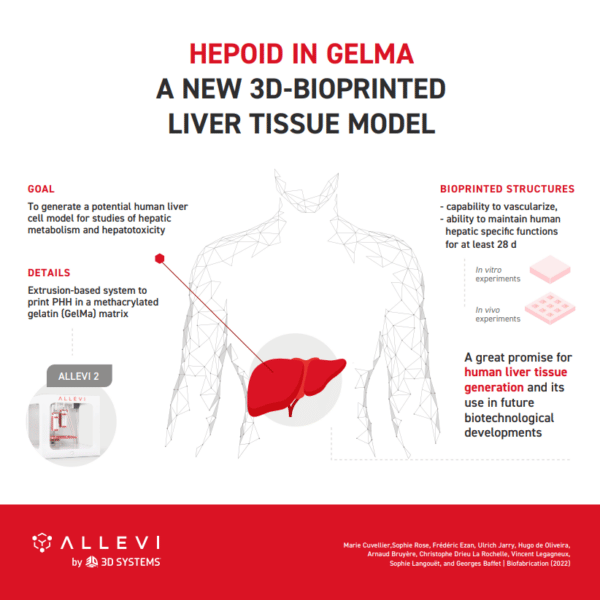
Hepoid in GelMA – A new 3D‐bioprinted liver tissue model
It is no surprise that recent advances in 3D cell culture models have greatly contributed to the understanding of organ function and disease, encouraging the development of new therapies. One

It is no surprise that recent advances in 3D cell culture models have greatly contributed to the understanding of organ function and disease, encouraging the development of new therapies. One
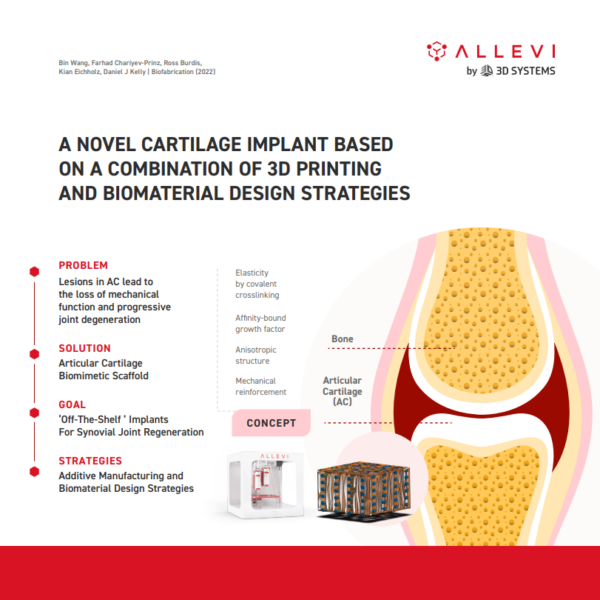
The field of regenerative medicine in joint disorders has progressed in the last month with help from researchers at Trinity College Dublin in Dublin, Ireland. Researchers from the Centre for
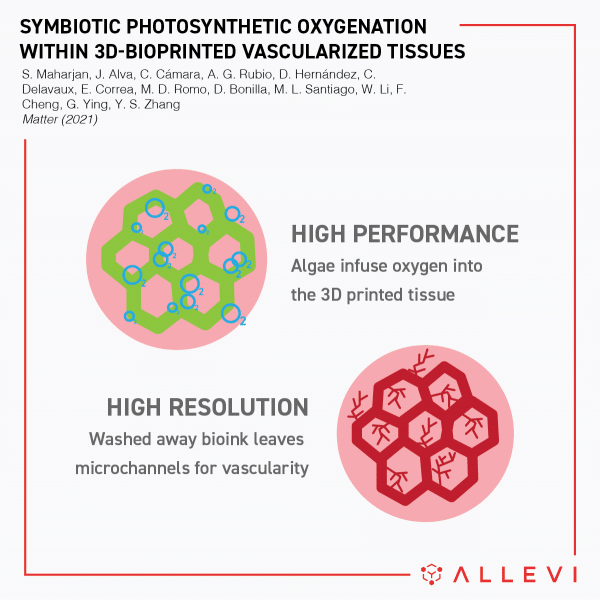
Engineers often rely on Mother Nature to help solve difficult problems. After millions of years of evolution, living organisms such as plants, animals, and microbes have discovered how to survive
The liver plays an incredibly important role in the human body by metabolizing drugs and other compounds. Developing accurate in vitro liver models to study is a critical step in
In their recent publication, Allevi authors, Abraham Samuel Finny, Cindy Jiang, and Silvana Andreescu developed a custom bioink which they can print into a skin safe UV sensor. Such a
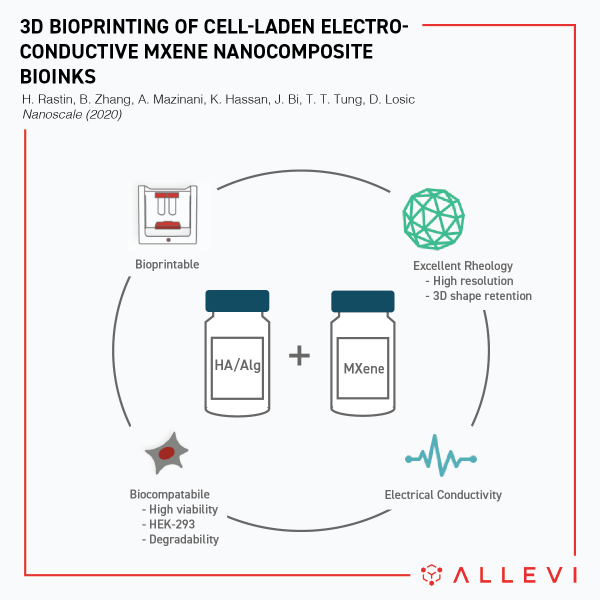
Hadi Rastin together with his colleagues from the University of Adelaide in Australia created a new electroconductive bioink that can be combined with cells and easily extruded with excellent results.
In their recent publication, Allevi authors Serkan Dikici, Fredrick Claeyssens, and Sheila MacNeil developed a very clever synthetic vascular network (SVN) by combining electro-spun layers with 3D bioprinted vascular channels.
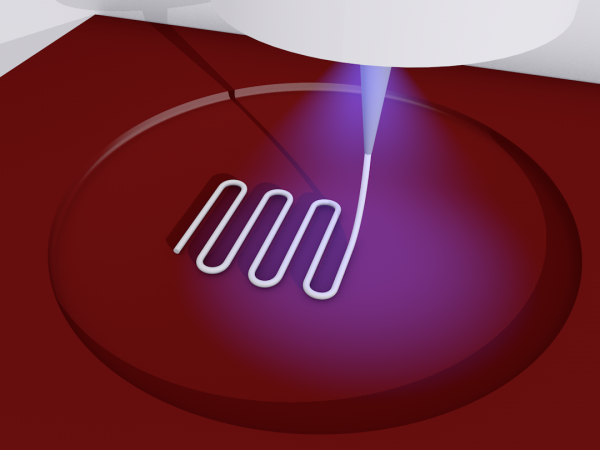
Bioprinting always requires consideration of many different parameters: biomaterial mechanical and biological properties, printability, cell viability and many more. It requires finding a fine balance between all the factors and

“Shrinking printing” opens the possibility to improve your 3D bioprinting resolution with quick and simple post-processing. If your goal is to create small channels, a fine mesh, or similar micro-geometries
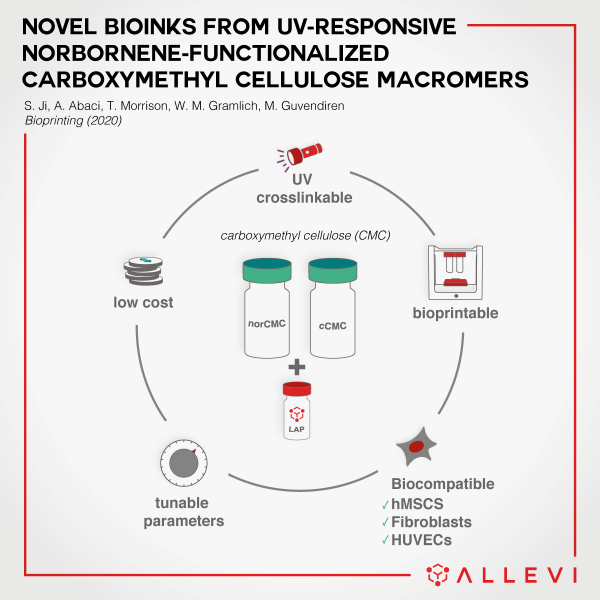
A bioprinted construct is only as good as the bioink used to create it. There are many biomaterial options available on the market, however, the need for more customized hydrogels
If stem cell therapies take off – we’re going to need a way to solve the stem cell supply problem – read on to learn more: The Promise We’ve all

We’re so excited to welcome the Yu Shrike Zhang lab from Brigham & Women’s Hospital to the Allevi Author Club! His new paper explores how porous is preferred when it